
The exception is hydrogen, which is on the top left of the table. Nonmetals are clustered in the upper right hand section of the periodic table. Metals tend to be good electrical and thermal conductors, hard, and shiny. Most other element groups have electron affinities lower than that of the halogens, but greater than the noble gases. Halogens (like chlorine and iodine) have high electron affinities. Noble gases (like argon and neon) have an electron affinity near zero and tend not to accept electrons. In addition to the information contained within the Periodic Table of Elements, the following articles may be helpful if you are writing a report about an. The ability to accept an electron, electron affinity can be predicted based on element groups.
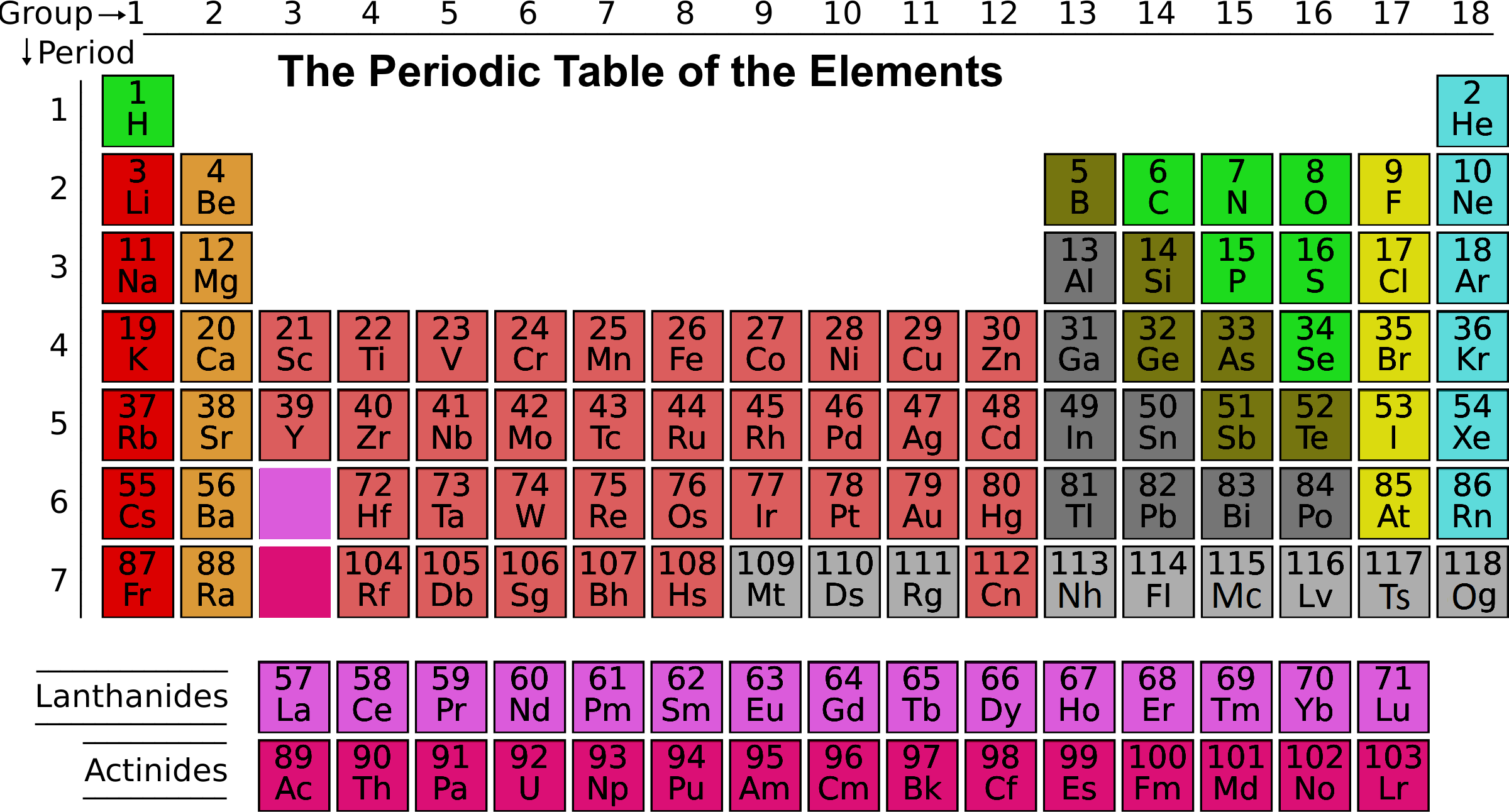
Each element in a group has the same number of valence electrons and typically behave in a similar manner when bonding with other elements. Mendeleev's original periodic table organized elements in order of increasing atomic mass or weight. When a range is given, it's because the abundance of isotopes varies from one sampling location to another. Other tables include two numbers, which represent a range of values. Sometimes a periodic table cites a single value for atomic weight. The element's atomic mass in atomic mass units is a weighted average mass of the element's isotopes. Changing number of electrons produces ions while changing the number of neutrons produces isotopes. Variation in the number of electrons or neutrons does not change the type of element. The number of protons is the deciding factor when distinguishing one element from another. The atomic number is how many protons an atom of that element contains. The modern periodic table is organized in order of increasing atomic number. Usually, the symbol is an abbreviation of the element name, but some symbols refer to older names of the elements (for example, the symbol for silver is Ag, which refers to its old name, argentum). Each symbol is either one or two letters in length. In some cases, the abbreviation comes from the element's Latin name. Each element's cell typically contains lots of important information about that element.Įlement symbols are abbreviations of the element's name. The periodic table is an arrangement of all the elements known to man in accordance with their increasing atomic number and recurring chemical properties. Elements that have similar chemical properties are.


Looking at carbon, for example, its symbol (C) and name appear, as well as its atomic number of six (in the upper left-hand corner) and its atomic mass of 12.11.The periodic table contains informative cells for each element arranged by increasing atomic number and chemical properties. A modern periodic table lists elements left to right by atomic number.

In addition to providing the atomic number for each element, the periodic table also displays the element’s atomic mass.
#Atomic table series
In the periodic table, shown in Figure 1, the elements are organized and displayed according to their atomic number and are arranged in a series of rows and columns based on shared chemical and physical properties. Elements also have specific chemical reactivity, the ability to combine and to chemically bond with each other. The properties of elements are responsible for their physical state at room temperature: they may be gases, solids, or liquids. Devised by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834–1907) in 1869, the table groups elements that, although unique, share certain chemical properties with other elements. The different elements are organized and displayed in the periodic table.
#Atomic table how to
Understand the periodic table of elements and how to use it to understand elements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
